By now many of you will probably have heard about Project “Acropolis” which was the code name for development where Nutanix decided to create an Uncompromisingly Simple management platform for an optimized KVM hypervisor.
Along the way with Nutanix extensive skills and experience with products such as vSphere and Hyper-V, we took on the challenge of delivering similar enterprise grade features while doing so in an equally scalable and performant platform as NDFS.
Acropolis therefore had to be built into PRISM. The below screen shot shows the Home screen for PRISM in a Nutanix Acropolis environment, looks pretty much the same as any other Nutanix solution right! Simple!
So let’s talk about how you install Acropolis. Since its a management platform for your Nutanix infrastructure it is critical component, so do I need a management cluster? No!
Acropolis is built into the Nutanix Controller VM (CVM), so it is installed by default when loading the KVM hypervisor (which is actually shipped by default).
Because its built into the CVM, Acropolis (and therefore all the management components) automatically scale with the Nutanix cluster, so there is no need to size the management infrastructure. There is also no need to license or maintain operating systems for management tools, further reducing cost and operational expense.
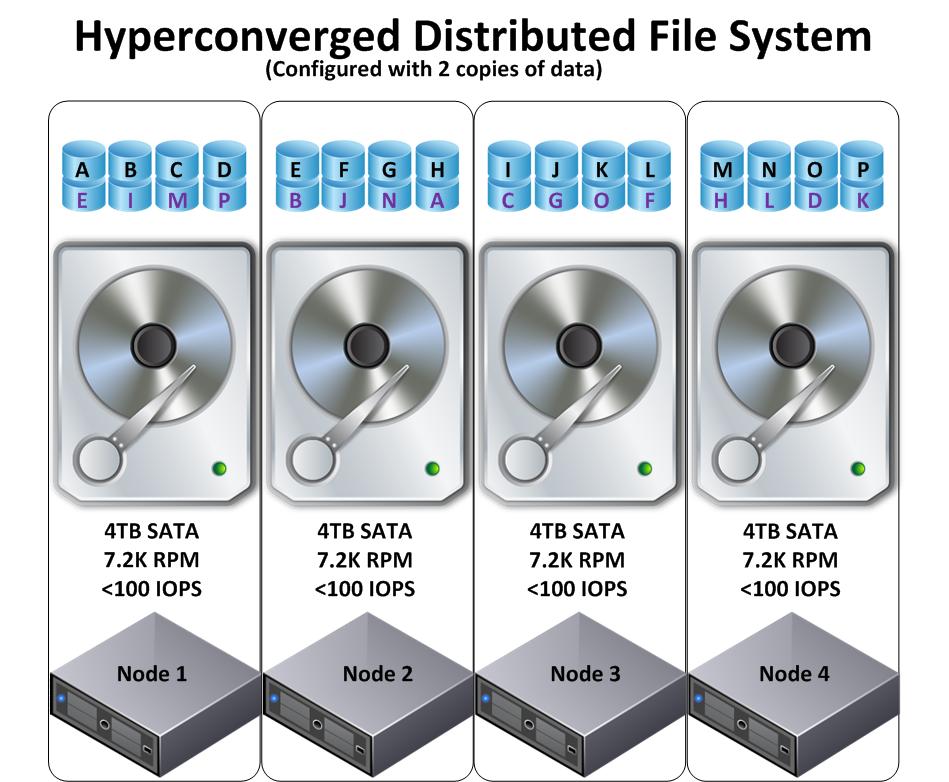
The following diagram shows a 4 node Nutanix NDFS cluster running Nutanix KVM Hypervisor using Acropolis. One CVM per cluster is elected the Acropolis Master and the rest of the CVMs are Acropolis Slaves.
The Acropolis Master is responsible for the following tasks:
- Scheduler for HA
- Network Controller
- Task Executors
- Collector/Publisher of local stats from Hypervisor
- VNC Proxy for VM Console connections
- IP address management
Each Acropolis Slave is responsible for the following tasks:
- Collector/Publisher of local stats from Hypervisor
- VNC Proxy for VM Console connections
Acropolis is a truly distributed management platform which has no dependency on external database servers and is fully resilient with in-built self healing capabilities so in the event of node or CVM failures that management continues without interruption.
What does Acropolis do? Well, put simply, the things 95% of customers need including but not limited to:
- High Availability (Think vSphere HA)
- Load Balancing / Virtual Machine Migrations (Think DRS & vMotion)
- Virtual machine templates
- Cloning (Instant and space efficient like VAAI-NAS)
- VM operations / snapshots / console access
- Centralised configuration of nodes (think vSphere Host Profiles & vSphere Distributed Switch)
- Centralized Managements of virtual networking (think vSphere Distributed Switch)
- Performance Monitoring of Physical HW, Hypervisor & VMs (think vRealize Operations manager)
Summary: Acropolis combines the best of breed hyperconverged platform with an enterprise grade KVM management solution which dramatically simplifies the design, deployment and ongoing management of datacenter infrastructure.
In the next few parts of this series I will explore the above features and the advantages of the Acropolis solution.