The Nutanix platform has and will continue to evolve to meet/exceed the ever increasing customer and application requirements while working within constraints such as licensing.
Two of the most common workloads which I work frequently with customers to design solutions around real or perceived licensing constraints are Oracle and SQL.
In years gone by, Nutanix solutions were constrained to being built around a limited number of node types. When I joined in 2013 only one type existed (NX-3450) which limited customers flexibility and often led to paying more for licensing than a traditional 3-tier solution.
With that said, the ROI and TCO for the Nutanix solutions back then were still more often than not favourable compared to 3-tier but these days we only have more and more good news for prospective and existing customers.
Nutanix has now rounded out the portfolio with the introduction of “Compute Only” nodes to target a select few niche workloads with real or perceived licensing and/or political constraints.
Compute only nodes compliment the traditional HCI nodes (Compute+Storage) as well as our unique Storage Only Nodes which were introduced in mid 2015.
So how do Compute Only nodes help solve these licensing challenges?
In short, Oracle leads the world in misleading and intimidating customers into paying more for licensing than what they need to. One of the most ridiculous claims is “You must license every physical CPU core in your cluster because Oracle could run or have ran on it”.
The below tweet makes fun of Oracle and shows how ridiculous their claim that customers need to license every node in a cluster (which I’ve never seen referenced in any actual contract) is.
So let’s get to how you can design a Nutanix solution to meet a typical Oracle customer licensing constraint while ensuring excellent Scalability, Resiliency and Performance.
At this stage we now assume you’ve given your first born child and left leg to Oracle and have subsequently been granted for example 24 physical core licenses from Oracle, what next?
If we we’re to use HCI nodes, some of the CPU would be utilised by the Nutanix Controller VM (CVM) and while the CVM does add a lot of value (see my post Cost vs Reward for the Nutanix Controller VM) you may be so constrained by licensing that you want to maximise the CPU power for just Oracle workloads.
Now in this example, we have 24 licensed physical cores, so we could use two Compute Only nodes using an Intel Gold 6128 [6 cores / 3.4 GHz] / 12 cores per server for 24 total physical cores.
Next we would assess the storage capacity, resiliency and performance requirements and decide how many and what configuration storage only nodes are required.
Because Virtual Machines cannot run on storage only nodes, the Oracle Virtual Machines cannot and will never run on any other CPU cores other than the two Compute Only nodes therefore you would be in compliance with your licensing.
The below is an example of what the environment could look like.

SQL has ever changing CPU licensing models which in some cases are licensed by server or vCPU count, Compute Only can be used in the same way I explained above to address any SQL licensing constraints.
What about if I need to scale storage capacity and/or performance?
You’re in luck, without any modifications to the Oracle workloads, you can simply add one or more storage only nodes to the cluster and it will almost immediately increase capacity, performance and resiliency!
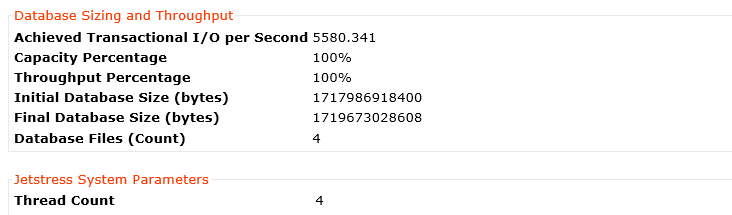
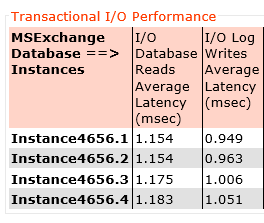
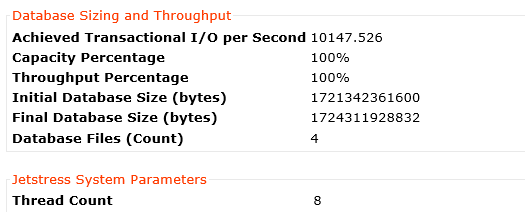
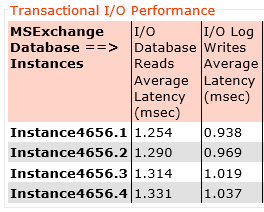
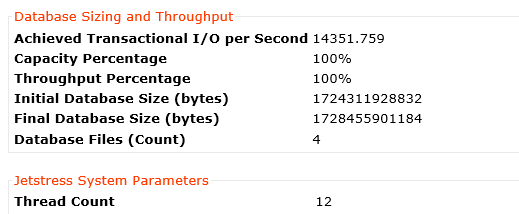
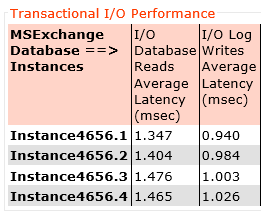
I’ve published an example of the performance improvement by adding storage only nodes to a cluster in an article titled Scale out performance testing with Nutanix Storage Only Nodes which I wrote back in 2016.
In short, the results show by doubling the number of nodes from 4 to 8, the performance almost exactly doubled while delivering low read and write latency.
What if you’ve already invested in Nutanix HCI nodes (example below) and are running Oracle/SQL or any other workloads on the cluster?

Nutanix provides the ability to convert a HCI node into a Storage Only node which results in preventing Virtual Machines from running on that node. So all you need to do is add two or more Compute Only nodes to the cluster, then mark the existing HCI nodes as Storage Only and the result is shown below.

This is in fact the minimum supported configuration for Compute Only Environments to ensure minimum levels of resiliency and performance. For more information, check out my post “Nutanix Compute Only Minimum requirements“.
Now we have two nodes (Compute Only) which can run Virtual Machines and four nodes (HCI nodes converted to Storage Only) which are servicing the storage I/O. In this scenario, if the HCI nodes have unused CPU and/or RAM the Nutanix Controller VM (CVM) can also be scaled up to drive higher performance & lower latency.
Compute Only is currently available with the Nutanix Next Generation Hypervisor “AHV”.
Now let’s cover off a few of the benefits of running applications like Oracle & SQL on Nutanix:
- No additional Virtualization licensing (AHV is included when purchasing Nutanix AOS)
- No rip and replace for existing HCI investment
- Unique scale out distributed storage fabric (ADSF) which can be easily scaled as required
- Storage Only nodes add capacity, performance and resiliency to your mission critical workloads without incurring additional hypervisor or application licensing costs
- Compute Only allows scale up and out of CPU/RAM resources where applications are constrained by ONLY CPU/RAM and/or application software licensing.
- Storage Only nodes can also provide functions such as Nutanix Files (previously known as Acropolis File Services or AFS)
As a result of Nutanix now having HCI, Storage Only and Compute Only nodes, we’re now entering the time where Nutanix can truely be the standard platform for almost any workload including those with non technical constraints such as political or application licensing which have traditionally been at least perceived to be an advantage for legacy SAN products.
The beauty of the Nutanix examples above is while they look like a traditional 3-tier, we avoid the legacy SAN problems including:
1. Rip and Replace / High Impact / High Risk Controller upgrades/scalability
2. Difficulty in scaling performance with capacity
3. Inability to increase resiliency without adding additional Silos of storage (i.e.: Another dual controller SAN)
With Compute Only being supported by AHV, we also help customers avoid the unnecessary complexity and related operational costs of managing ESXi deployments which have become increasingly more complex over time without significantly improving value to the average customer who simply wants high performance, resilient and easy to manage virtualisation solution.
But what about VMware ESXi customers?
Obviously moving to AHV would be ideal but for those who cannot for whatever reasons can still benefit from Storage Only nodes which provide increased storage performance and resiliency to the Virtual machines running on ESXi.
Customers can run ESXi on Nutanix (or OEM / Software Only) HCI nodes and then scale the clusters performance/capacity with AHV based storage only nodes, therefore eliminating the need to license both ESXi and Oracle/SQL since no virtual machine will run on these nodes.
How does Nutanix compare to a leading all flash array?
For those of you who would like to see a HCI only Nutanix solution have better TCO as well as performance and capacity than a leading All Flash Array, checkout A TCO Analysis of Pure FlashStack & Nutanix Enterprise Cloud where even with giving every possible advantage to Pure Storage, Nutanix still comes out on top without data reduction assumptions.
Now consider that Nutanix the TCO as well as performance and capacity was better than a leading All Flash Array with only HCI nodes, imagine the increased efficiency and flexibility by being able to mix/match HCI, with Storage Only and Compute only.
This is just another example of how Nutanix is eliminating even the corner use cases for traditional SAN/NAS.
For more information about Nutanix Scalability, Resiliency and Performance, checkout this multi-part blog series.